RxJS first steps - Subject and ReplaySubject

I’m not sure you already heard about RxJS or Reactive Programming in general. There’s currently a very strong movement towards such programming style in the modern JavaScript world, so you should definitely check it out. Here we’re going to take a look at a very specific part of RxJS 5, namely Subject and ReplaySubject by implementing a simple publish/subscriber mechanism. (TL;DR: check out the screencast at the end)
Contents are based on Angular version >= 2
So a couple of days ago I read this Tweet:
@amcdnl RxJS is just like linq or lodash. Use the operators you need and forget the rest.
— Cecil L. Phillip (@cecilphillip) June 3, 2016
I totally agree, RxJS has a “learning cliff” :smiley:
#gotoams RxJS learning curve? No.. Learning cliff! pic.twitter.com/vWgYI09ar1
— Patrick Kiernan (@hoss) June 14, 2016
But I think Cecil’s answer is an awesome way to approach this initial complexity. Take what you need, learn about it, use it and move on. Don’t worry to understand everything at once (it’s overwhelming, I promise!). Coming from the .Net world, I remember when I first got in touch with Linq, a querying language built into .Net, that allows to write really powerful queries over collections, even over database objects (via appropriate adapters). It seemed so odd..complex, but once you grasp it, it’s just mind blowing powerful. I have the feeling the same holds for RxJS.
What I needed: a broadcasting mechanism
So I’m having an Angular 1.x application and I needed a way for other (potentially lazy loaded) components to get notified about certain events happening within the application. Like, whenever the user executes a search through the application’s search component, I want such modules to allow to subscribe to a “search event” and then get invoked with the search results.
Angular 1? Why don’t you simply use the
$rootScope.$emit(…)as broadcasting mechanism? Sure thing, that would totally work. But under the assumption that I’ll upgrade sooner or later to Angular, I’m trying to avoid the$scopeas much as possible. Also it has other side effects as well.
RxJS is made for this, right? There’s a stream of data (my broadcast values), and there are so-called Observables to which you can subscribe and get updated about new values. I always wanted to experiment around with RxJS on a concrete example, so it was time.
First things first. What is RxJS? What am I talking about?

RxJS is the JavaScript implementation of ReactiveX.
ReactiveX is more than an API, it’s an idea and a breakthrough in programming. It has inspired several other APIs, frameworks, and even programming languages. reactivex.io
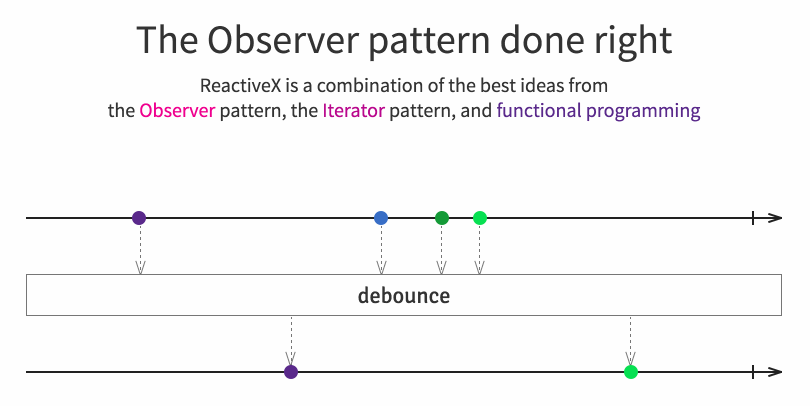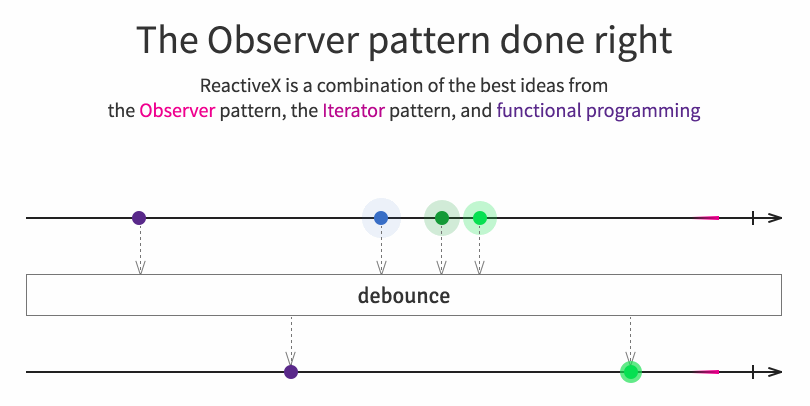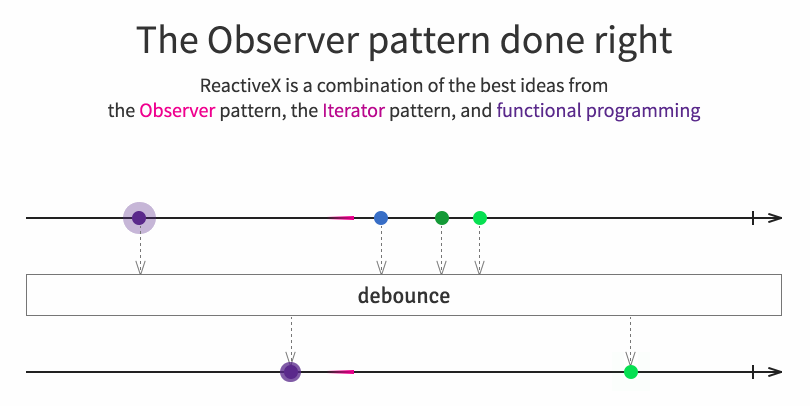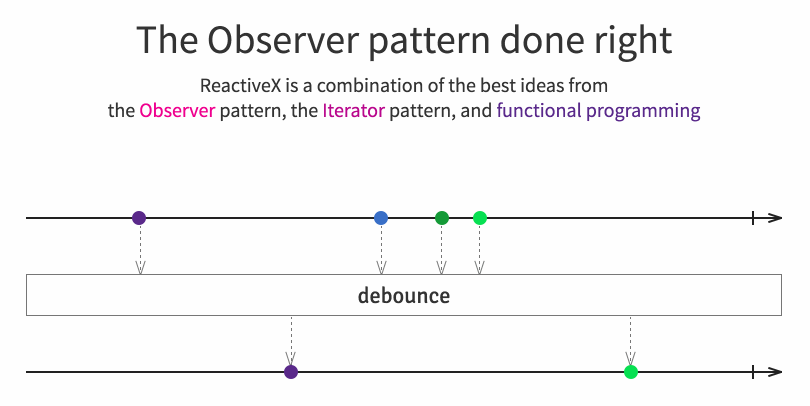
It implements concepts from the popular observer pattern, iterator pattern and functional programming. Usually, using a reactive extension library consists in creating some kind of event stream, then combining/transforming those streams with query like operators and finally to listen by subscribing to those resulting streams for performing operations. Browse the official site for more details.
It has initially been popularized by Microsoft and published under the Reactive-Extensions GitHub repository, containing various language specific implementations. In fact, when you google for RxJS (the JavaScript implementation of reactive extensions), you most probably land on the GitHub repo of RxJS 4. Recently, this library has been rewritten from ground up with performance in mind: the result is RxJS 5 (beta). Core contributor here is Ben Lesh, senior software engineer at Netflix, which is a huge consumer of Rx (and stands for everything performance related).
@juristr 5 is a total rewrite with a focus on compatibility with the ECMAScript proposal, as well as performance improvements
— Ben Lesh (@BenLesh) June 18, 2016
With Angular, also Google jumped onto reactive extensions. Angular makes heavy use of RxJS 5, for instance the provided http library returns Rx Observables by default, rather than Promises as you might expect.
Also, Twitter is an awesome source of information (at least for me). So if you want to get more on Reactive programming I recommend you to go and follow these guys:
- Ben Lesh - Software Engineer at Netflix in charge of RxJS 5
- Andre Staltz - A reactive programming and functional programming expert which has written THE introduction to reactive programming (see link at end of this article)
- Michel Weststrate - Creator of MobX, a state management library that embraces reactive programming like no other lib
- Rob Wormald - Developer advocate at Google on the Angular team and big proponent of reactive programming. He also created ngrx, a project that started as a Redux inspired library built with RxJS and evolved to a collection of reactive extensions for Angular.
- Victor Savkin - Developer advocate at Google on the Angular team. On his blog he writes interesting articles, also on reactive programming, in particular this one.
- and probably many others. Let me know and I’ll list them here :smiley:
Subject and ReplaySubject
Rx.Subject: “Represents an object that is both an observable sequence as well as an observer. Each notification is broadcasted to all subscribed observers.”
That sounds good for our broadcasting mechanism, right? We’re not so much interested in the “observer” part of the Subject but in the fact it is an “observable sequence”. Great, so let’s create a new instance of it.
var broadcast = new Rx.Subject();From here you can start emitting new values using the next(..) function, like
broadcast.next('Hi there');
broadcast.next('Anyone??');Now obviously someone needs to “listen” to these broadcasts and do something with these values. That’s what we call “subscribe”.
var someSubscriber = broadcast
.subscribe(function(value) {
console.log('Got value: ' + value);
});That was easy right? Obviously we can broadcast any kind of value we need. Great! But now we’re going to make things a bit more interesting and realistic. In our app subscribers may come in and go at different times. So I created a simple UI that allows to simulate such behavior. Something like this:

We don’t have to change much in our code. Just some HTML and we move the value emitting inside a button click:
addClickListener('broadcastValue', function() {
broadcast.next('Broadcasting..' + Math.round((Math.random() * 100)));
});Also the subscribers are registered when the corresponding button is clicked:
addClickListener('subs1', function() {
broadcast.subscribe(function(value) {
print('Subs1 got ' + value);
});
});Btw, addClickListener is just a helper function I created.
Note, if you just click the “Broadcast value” button without registering a subscriber, nothing happens. Once you start clicking a subscriber or two, they’ll start receiving the values and start printing them out.
Can we also unsubscribe??
Of course. subscribe() returns a reference on which we can invoke unsubscribe().
var subscriber = broadcast.subscribe(...);
...
// unsubscribe again
subscriber.unsubscribe();Nice 👍.
What if I want to subscribe only to specific events?
In a publish/subscribe environment my modules in the application might only be interested in certain kind of events and not all of them. Obviously we could take them out in the subscribe(...). But there’s a more powerful mechanism built into RxJS: lots of operators! We’re interested in the filter operation here.
Like, we want subscriber 1 to only get values < 50.
sub1Subscription =
broadcast
.filter(function(value){
return value < 50;
})
.subscribe(function(value) {
print('Subs1 got ' + value);
});If you’re using ES6, it looks even cleaner:
sub1Subscription =
broadcast
.filter(x => x < 50)
.subscribe(x => print('Subs1 got ' + value));Here we go:
Wait, you also mentioned ReplaySubject? What’s the difference?
“ReplaySubject emits to any observer all of the items that were emitted by the source Observable(s), regardless of when the observer subscribes.” ReactiveX Docs
Interesting, let’s try that out. We do nothing else other than changing the Subject with ReplaySubject:
var broadcast = new Rx.ReplaySubject();
...Now, in the example below, click the broadcast button a couple of times and then click on an subscriber button to register it. Note that it’ll immediately start writing out values which have been published previously.
Besides Subject which is the most basic one and ReplaySubject, there exist also others like AsyncSubject and BehaviorSubject. Simple google for examples on those.
Conclusion
We obviously only scratched the surface here. RxJS is extremely powerful, especially when combined with asynchronous data “flowing in from your APIs”. It’s hard to get started initially, but I highly recommend you to play around with it, use my JSBins above, clone them and experiment.
Also, I’ve not yet tried it, but the above described approach could be a very valid alternative for replacing Angular 1.x’s $rootScope.$emit and $rootScope.$broadcast for broadcasting. That would further help to avoid using the $scope and prepare for a migration to Angular. Idea for another post 😉.
Here are some further, related links.
Reactive Programming with RxJs 5 and Http in Angular
André Staltz introduces the very basics of what reactive programming is all about.
A complete list of RxJS 5 operators with easy to understand explanations and runnable examples.

Observables are great for building UIs and RxJS is an amazing implementation of them. Despite the library's awesome power, it’s relatively underutilized mostly due to it being hard. This talk gives a high level overview of what observables are, how you use them, and why they are useful, through a basic implementation and a real world example (searching reddit for cute animals).
In this article I will introduce four independent dimensions of reactive programming